Linear temporal logic
In logic, Linear temporal logic (LTL) is a modal temporal logic with modalities referring to time. In LTL, one can encode formulae about the future of paths such as that a condition will eventually be true, that a condition will be true until another fact becomes true, etc. It is a fragment of the more complex CTL*, which also allows branching time and quantifiers. Subsequently LTL is sometimes called propositional temporal logic, abbreviated PTL.[1] Linear temporal logic (LTL) is a fragment of S1S.
LTL was first proposed for the formal verification of computer programs by Amir Pnueli in 1977.[2]
Contents |
Syntax
LTL is built up from a finite set of propositional variables AP, the logical operators ¬ and ∨, and the temporal modal operators X and U. Formally, the set of LTL formulas over AP is inductively defined as follows:
- if p ∈ AP then p is a LTL formula;
- if ψ and φ are LTL formulas then ¬ψ, φ ∨ ψ, X ψ and φ U ψ are LTL formulas.[3]
X is read as next and U is read as until. Sometimes, N is also used in place of X. Other than these fundamental operators, there are additional logical and temporal operators defined in terms of the fundamental operators to write LTL formulas succinctly. The additional logical operators are ∧, →, ↔, true, and false. Following are the additional temporal operators.
- G for always (globally)
- F for eventually (in the future)
- R for release
- W for weakly until
Semantics
An LTL formula can be satisfied by an infinite sequence of truth evaluations of variables in AP. This sequences can be viewed as a word on a path of a Kripke structure (an ω-word over alphabet 2AP). Let w=a1,a2,a3,... be such ω-word. Let w(i) = ai. Let wi = ai,ai+1,... , which is a suffix of w. Formally, the satisfaction relation 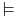 between a word and an LTL formula is defined as follows:
between a word and an LTL formula is defined as follows:
- w
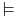 p if p ∈ w(1)
p if p ∈ w(1) - w
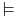 ¬ψ if w
¬ψ if w 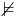 ψ
ψ - w
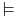 φ ∨ ψ if w
φ ∨ ψ if w 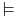 φ or w
φ or w 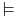 ψ
ψ - w
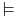 X ψ if w2
X ψ if w2 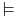 ψ (in the next time step ψ must be true)
ψ (in the next time step ψ must be true) - w
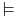 φ U ψ if there exist i > 0 such that wi
φ U ψ if there exist i > 0 such that wi 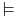 ψ and for all 0 < k < i, wk
ψ and for all 0 < k < i, wk 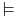 φ (φ must remain true until ψ becomes true)
φ (φ must remain true until ψ becomes true)
We say an ω-word w satisfies LTL formula ψ when w 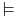 ψ. The ω-language L(ψ) defined by ψ is the set {w | w
ψ. The ω-language L(ψ) defined by ψ is the set {w | w 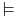 ψ} of ω-words that satisfy ψ. A formula ψ is satisfiable if there exist a ω-word w such that w
ψ} of ω-words that satisfy ψ. A formula ψ is satisfiable if there exist a ω-word w such that w 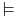 ψ. A formula ψ is valid if for each ω-word w over alphabet 2AP, w
ψ. A formula ψ is valid if for each ω-word w over alphabet 2AP, w 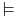 ψ.
ψ.
The additional logical operators are defined as follows:
- φ ∧ ψ ≡ ¬(¬φ ∨ ¬ψ)
- φ → ψ ≡ ¬φ ∨ ψ
- φ ↔ ψ ≡ (φ → ψ) ∧ ( ψ → φ)
- true ≡ p ∨ ¬p, where p ∈ AP
- false ≡ ¬true
The additional temporal operators R, F, and G are defined as follows:
- φ R ψ ≡ ¬(¬φ U ¬ψ) ( ψ remains true until once φ becomes true. φ may never become true)
- F ψ ≡ true U ψ (eventually ψ becomes true)
- G ψ ≡ false R ψ ≡ ¬F ¬ψ (ψ always remains true)
- Weak until
Some authors also define a weak until binary operator, denoted W, with semantics similar to that of the until operator but the stop condition is not required to occur (similar to release).[4] It is sometimes useful since both U and R can be defined in terms of the weak until:
- φ W ψ ≡ (φ U ψ) ∨ G φ ≡ φ U (ψ ∨ G φ) ≡ ψ R (ψ ∨ φ)
- φ U ψ ≡ Fψ ∧ (φ W ψ)
- φ R ψ ≡ ψ W (ψ ∧ φ)
The semantics for the temporal operators are pictorially presented as follows.
| Textual | Symbolic† | Explanation | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unary operators: | |||
X  |
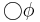 |
neXt:  has to hold at the next state. has to hold at the next state. |
|
G  |
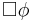 |
Globally:  has to hold on the entire subsequent path. has to hold on the entire subsequent path. |
|
F  |
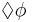 |
Finally:  eventually has to hold (somewhere on the subsequent path). eventually has to hold (somewhere on the subsequent path). |
|
| Binary operators: | |||
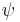 U U  |
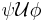 |
Until: 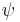 has to hold at least until has to hold at least until  , which holds at the current or a future position. , which holds at the current or a future position. |
|
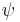 R R  |
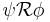 |
Release:  has to be true until and including the point where has to be true until and including the point where 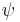 first becomes true; if first becomes true; if 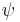 never becomes true, never becomes true,  must remain true forever. must remain true forever. |
|
†The symbols are used in the literature to denote these operators.
Equivalences
Let Φ, ψ, and ρ be LTL formulas. The following tables list some of the useful equivalences which extend standard equivalences among the usual logical operators.
| Distributivity | ||
|---|---|---|
| X (Φ ∨ ψ) ≡ (X Φ) ∨ (X ψ) | X (Φ ∧ ψ)≡ (X Φ) ∧ (X ψ) | X (Φ U ψ)≡ (X Φ) U (X ψ) |
| F (Φ ∨ ψ) ≡ (F Φ) ∨ (F ψ) | G (Φ ∧ ψ)≡ (G Φ) ∧ (G ψ) | |
| ρ U (Φ ∨ ψ) ≡ (ρ U Φ) ∨ (ρ U ψ) | (Φ ∧ ψ) U ρ ≡ (Φ U ρ) ∧ (ψ U ρ) | |
| Negation propagation | ||
|---|---|---|
| ¬X Φ ≡ X ¬Φ | ¬G Φ ≡ F ¬Φ | ¬F Φ ≡ G ¬Φ |
| ¬ (Φ U ψ) ≡ (¬Φ R ¬ψ) | ¬ (Φ R ψ) ≡ (¬Φ U ¬ψ) | |
| Special Temporal properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| F Φ ≡ F F Φ | G Φ ≡ G G Φ | Φ U ψ ≡ Φ U (Φ U ψ) |
| Φ U ψ ≡ ψ ∨ ( Φ ∧ X(Φ U ψ) ) | Φ W ψ ≡ ψ ∨ ( Φ ∧ X(Φ W ψ) ) | Φ R ψ ≡ ( ψ ∧ (Φ ∨ X(Φ R ψ) ) |
| G Φ ≡ Φ ∧ X(G Φ) | F Φ ≡ Φ ∨ X(F Φ) | |
Negation normal form
All the formulas of LTL can be transformed into negation normal form, where
- all negations appear only in front of the atomic propositions,
- only other logical operators true, false, ∧, and ∨ can appear, and
- only the temporal operators X, U, and R can appear.
Using the above equivalences for negation propagation, it is possible to derive the normal form. This normal form allows R, true, false, and ∧ to appear in the formula, which are not fundamental operators of LTL. Note that the transformation to the negation normal form does not blow up the size of the formula. This normal form is useful in translation from LTL to Büchi automaton.
Relations with other logics
LTL can be shown to be equivalent to the monadic first-order logic of order, FO[<]—a result known as Kamp's theorem—[5] or equivalently star-free languages.[6]
Computation tree logic (CTL) and Linear temporal logic (LTL) are both a subset of CTL*. CTL and LTL are not equivalent and they have a common subset, which is a proper subset of both CTL and LTL. For example,
- No formula in CTL can define the language that is defined by LTL formula G(F p).
- No formula in LTL can define the language that is defined by CTL formula AG( p → (EXq ∧ EX¬q) ).
Applications
- Automata theoretic Linear temporal logic model checking
An important way to model check is to express desired properties (such as the ones described above) using LTL operators and actually check if the model satisfies this property. One technique is to obtain a Büchi automaton that is "equivalent" to the model and one that is "equivalent" to the negation of the property. The intersection of the two non-deterministic Büchi automata is empty if the model satisfies the property.[7]
- Expressing important properties in formal verification
There are two main types of properties that can be expressed using linear temporal logic: safety properties usually state that something bad never happens (G
 ), while liveness properties state that something good keeps happening (GF
), while liveness properties state that something good keeps happening (GF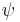 or G
or G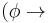 F
F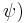 ). More generally: Safety properties are those for which every counterexample has a finite prefix such that, however it is extended to an infinite path, it is still a counterexample. For liveness properties, on the other hand, every finite prefix of a counterexample can be extended to an infinite path that satisfies the formula.
). More generally: Safety properties are those for which every counterexample has a finite prefix such that, however it is extended to an infinite path, it is still a counterexample. For liveness properties, on the other hand, every finite prefix of a counterexample can be extended to an infinite path that satisfies the formula.
- Specification language
One of the applications of linear temporal logic is the specification of preferences in the Planning Domain Definition Language for the purpose of preference-based planning.
See also
References
- ^ Dov M. Gabbay, A. Kurucz, F. Wolter, M. Zakharyaschev (2003). Many-dimensional modal logics: theory and applications. Elsevier. p. 46. ISBN 9780444508263. http://books.google.com/books?id=P8jZwiExZYEC&pg=PA46.
- ^ Amir Pnueli, The temporal logic of programs. Proceedings of the 18th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS), 1977, 46–57. doi:10.1109/SFCS.1977.32
- ^ Sec. 5.1 of Christel Baier and Joost-Pieter Katoen, Principles of Model Checking, MIT Press [1]
- ^ Sec. 5.1.5 "Weak Until, Release, and Positive Normal Form" of Principles of Model Checking.
- ^ http://books.google.com/books?id=TLpcI2axv8kC&pg=PA22
- ^ Moshe Y. Vardi (2008). "From Church and Prior to PSL". In Orna Grumberg, Helmut Veith. 25 years of model checking: history, achievements, perspectives. Springer. ISBN 9783540698494. preprint
- ^ Moshe Y. Vardi. An Automata-Theoretic Approach to Linear Temporal Logic. Proceedings of the 8th Banff Higher Order Workshop (Banff'94). Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 1043, pp. 238--266, Springer-Verlag, 1996. ISBN 3-540-60915-6.
- External links
- A presentation of LTL
- Linear-Time Temporal Logic and Büchi Automata
- LTL Teaching slides of professor Alessandro Artale at the Free University of Bozen-Bolzano
- LTL to Buchi translation algorithms a genealogy, from the website of Spot a library for model-checking.